To become a medical doctor in the United States, you’ll need to:
- Earn a bachelor’s degree: A degree in a health-related field, such as biology, biochemistry, or exercise science, can help prepare you for medical school. The degree you choose should be accredited to ensure that the credits count toward medical school.
- Take the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT): This multi-choice exam is created by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). Almost all medical schools in the US require applicants to submit their MCAT scores.
- Complete medical school: This takes an additional four years.
- Complete a residency: This is a required internship that allows you to practice medicine while training under established doctors. The length of your residency depends on your chosen specialty and can range from three to seven years.
- Consider a fellowship: A fellowship is optional additional training that allows you to sub-specialize and train with top physicians in your field. Fellowships can be selective and can create more job opportunities.
- Earn certifications: Depending on your speciaTo become a medical doctor in the United States, you’ll need to:
- Earn a bachelor’s degree: A degree in a health-related field, such as biology, biochemistry, or exercise science, can help prepare you for medical school. The degree you choose should be accredited to ensure that the credits count toward medical school.
- Take the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT): This multi-choice exam is created by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). Almost all medical schools in the US require applicants to submit their MCAT scores.
- Complete medical school: This takes an additional four years.
- Complete a residency: This is a required internship that allows you to practice medicine while training under established doctors. The length of your residency depends on your chosen specialty and can range from three to seven years.
- Consider a fellowship: A fellowship is optional additional training that allows you to sub-specialize and train with top physicians in your field. Fellowships can be selective and can create more job opportunities.
- Earn certifications: Depending on your specialty, you can earn certifications from the American Board of Medical Specialties. These certifications can help improve your qualifications when looking for a job.
- Most Physicians and Specialists follow this step-by-step approach.
- MEDICAL SCHOOL. Complete a post-graduate degree in medicine, achieving either a medical doctor or doctor of osteopathy degree.
- LICENSURE. Pass state licensing exams and national boards! Each State Has Requirements! Check the State Board Of Medicine in your State!
- RESIDENCY. Usually a Medical Facility is associated with the Medical School which you attended where you may complete your Residency!
You may also apply for Residency at another Facility when Available and you are accepted! - CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION. Each State has a Board Certification Examination to Earn Qualification as a Medical Doctor or a Doctor of Osteopathy!
- BOARD CERTIFICATION. You must apply to the various Boards that provide Specialty Qualification Exams!
- SUBSPECIALTY EXAM AND CERTIFICATION. When passing your Specialty Exam, The Board provides you the Certificate of Specialty! Filing with your State of Practice is required!
- CONTINUING CERTIFICATION. All States require proof of time spent in Medical or Specialty Practice! Reports of Certification may be required each one or 2 years!
To become a doctor of osteopathic medicine (DO) in the United States, you must:
- Earn a bachelor’s degree from an accredited college or university
- Pass the Medical College Admissions Test (MCAT)
- Enroll in an osteopathic medical school
- Complete four years of medical school
- Pass Specialty Exam and Certification!
- Complete three to nine years of internships and residencies
- Pass state licensing exams and national boards
- Apply for licensure in your state
- Continuing Certification
Details for the above steps are as presented before!
Osteopathic medical schools are accredited by the Commission on Osteopathic College Accreditation (COCA). You can apply to all schools of interest using the American Association of Colleges of Osteopathic Medicine Application Service (AACOMAS).
DOs receive the same residency training as doctors of medicine (MDs), also known as allopathic physicians. They earn their licenses to practice medicine and can see patients and prescribe medication.
Osteopathic medicine is a philosophy and practice of physician care that emphasizes a whole-person approach, prevention, and wellness. DOs consider the connection of body, mind, and spirit in delivering care.
Doctor Specialty Information
Doctor of Medicine or Osteopathy

Doctor of Medicine or Osteopathy! Doctors of medicine (MDs) diagnose and treat illnesses, and perform a variety of other duties, including:
- Ordering, performing, and interpreting diagnostic tests, such as X-rays and lab work
- Prescribing medications and other treatments
- Managing a patient’s care
- Performing operations (surgeons)
- Examining patients
- Taking medical histories
- Counseling patients on diet, hygiene, and preventive healthcare
- DO’s ADD Maliputive Medicine (OMM) and a whole-person approach for prevention of illnesses, Creating Physical Wellness, and Mental Well Being.
MDs are allopathic doctors, which means they use conventional medical tools like X-rays, prescription drugs, and surgery for healing. They can specialize in many areas, including: Surgery, Specific body parts or organs, Psychiatry, Pediatrics Medicine(0 to 20 years), Humanatric Medicine (20 years to 60 years), and Geriatric medicine(60 years to 120 years)!
MDs and doctors of osteopathic medicine (DOs) are both licensed to practice medicine in all 50 states. They receive similar medical school education and train together in residency programs. The main difference is that DOs also receive extra training in Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine (OMM), a hands-on method for diagnosing and treating patients. They may Specialize as MD.s do!
SPECIALIZATIONS:
- Aerospace Medicine Specialist.
 Aerospace Medicine Specialist. Aerospace Medical Practitioners have an exclusive focus on preserving the physical and mental well-being of pilots, cosmonauts, and other experts who operate in aviation. These experts appraise and regulate medical conditions that may compromise their abilities, devise proactive solutions, and extend occupational welfare and security guidance. In addition, they can provide counsel on aviation human factors and scrutinize the impact of environmental conditions on human performance. To become an Aerospace Medicine Specialist, one must complete medical school (MD or DO), followed by a residency in preventive medicine or another primary specialty, and then a fellowship in aerospace medicine. Board certification is available through the American Board of Preventive Medicine.
Aerospace Medicine Specialist. Aerospace Medical Practitioners have an exclusive focus on preserving the physical and mental well-being of pilots, cosmonauts, and other experts who operate in aviation. These experts appraise and regulate medical conditions that may compromise their abilities, devise proactive solutions, and extend occupational welfare and security guidance. In addition, they can provide counsel on aviation human factors and scrutinize the impact of environmental conditions on human performance. To become an Aerospace Medicine Specialist, one must complete medical school (MD or DO), followed by a residency in preventive medicine or another primary specialty, and then a fellowship in aerospace medicine. Board certification is available through the American Board of Preventive Medicine.
> - Allergist.
 Allergist. An allergist is a healthcare professional who specializes in identifying and treating asthma, inherited immunodeficiency diseases, autoimmune diseases, allergies due to animals, foods, or medications, and related diseases. In addition to that, an allergist is also trained in determining the factors that trigger such diseases.
Allergist. An allergist is a healthcare professional who specializes in identifying and treating asthma, inherited immunodeficiency diseases, autoimmune diseases, allergies due to animals, foods, or medications, and related diseases. In addition to that, an allergist is also trained in determining the factors that trigger such diseases. How to become an allergist?
How to become an allergist?
> - Anesthesiologist
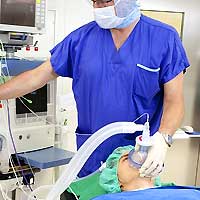 Anesthesiologist. Anesthesiologists play a major decisive role in pain management. As their name suggests, anesthesiologists are physicians trained in anesthesiology, or the science of administering anesthesia to patients during surgeries. Before (most) surgeries, anesthesia is given to relieve the pain or put them to sleep during the operation.
Anesthesiologist. Anesthesiologists play a major decisive role in pain management. As their name suggests, anesthesiologists are physicians trained in anesthesiology, or the science of administering anesthesia to patients during surgeries. Before (most) surgeries, anesthesia is given to relieve the pain or put them to sleep during the operation.
Pain management specialist (Anesthesiologist) is a medical doctor who helps patients with ongoing pain management for chronic conditions.- Pediatric Anesthesiologists specialize in providing anesthesia and pain management for children undergoing surgery or other medical procedures. They tailor anesthesia plans according to a child’s unique needs and monitor the child’s vital signs throughout the procedure.Cardiothoracic Anesthesiologists provide anesthesia and pain management for patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery, such as heart or lung operations. They collaborate with surgeons and monitor the patient’s vital signs during the procedure.Obstetric Anesthesiologists specialize in providing anesthesia and pain management for women during labor and delivery. They administer epidurals, spinal blocks, and other forms of anesthesia to ensure a comfortable and safe birth experience.Neuroanesthesiologists provide anesthesia and pain management for neurosurgery patients, such as brain or spinal cord procedures. They collaborate with neurosurgeons and monitor the patient’s neurological function during surgery.Regional Anesthesiologists specialize in providing anesthesia to specific body regions, such as the limbs or the torso, using nerve blocks and other techniques. This allows for targeted pain relief during and after surgery.
 How to become an Anesthesiologist?
How to become an Anesthesiologist?
> - Andrologist
 Andrologist. An Andrologist is the male equivalent of a gynecologist; they are concerned with helping their male patients with urological, sexual, and reproductive health that are unique to men. Interestingly, unlike gynecology, which requires plenty of medical board certification programs worldwide, andrology has no such requirements. Andrology has only been studied as a separate specialty since the late 1960s.
Andrologist. An Andrologist is the male equivalent of a gynecologist; they are concerned with helping their male patients with urological, sexual, and reproductive health that are unique to men. Interestingly, unlike gynecology, which requires plenty of medical board certification programs worldwide, andrology has no such requirements. Andrology has only been studied as a separate specialty since the late 1960s. How to become an Andrologist?
How to become an Andrologist?
> - Cardiologist
 Cardiologist. Cardiologists are medical professionals that examine and treat illnesses associated with the cardiovascular system which includes the heart and blood vessels. They also help their patients learn about their risk factors for heart disease and determine what treatment or procedure they should undergo. A pediatric cardiologist is a specialized physician within cardiology who treats and diagnoses heart complications in children. Cardiac surgeons who specialize in cardiac catheterization, angioplasty, and stenting treatment and diagnosis are usually called Interventional cardiologists.
Cardiologist. Cardiologists are medical professionals that examine and treat illnesses associated with the cardiovascular system which includes the heart and blood vessels. They also help their patients learn about their risk factors for heart disease and determine what treatment or procedure they should undergo. A pediatric cardiologist is a specialized physician within cardiology who treats and diagnoses heart complications in children. Cardiac surgeons who specialize in cardiac catheterization, angioplasty, and stenting treatment and diagnosis are usually called Interventional cardiologists.  How to become a Cardiologist?
How to become a Cardiologist?
> - Cardiac Electrophysiologist
 Cardiac Electrophysiologist. A Cardiac Electrophysiologist (EP) is a cardiologist who is specialized in the heart’s electrical system that includes treating heart rhythm issues such as atrial fibrillation. In many countries, Cardiac electrophysiology is viewed as a sub-discipline of cardiology and internal medicine (only from the 1970s). It typically requires 2+ years of internship training after a general cardiology fellowship.
Cardiac Electrophysiologist. A Cardiac Electrophysiologist (EP) is a cardiologist who is specialized in the heart’s electrical system that includes treating heart rhythm issues such as atrial fibrillation. In many countries, Cardiac electrophysiology is viewed as a sub-discipline of cardiology and internal medicine (only from the 1970s). It typically requires 2+ years of internship training after a general cardiology fellowship.  How to become a Cardiac Electrophysiologist?
How to become a Cardiac Electrophysiologist?
> - Dermatologist
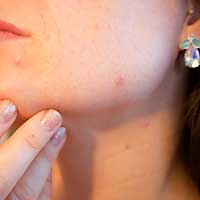 Dermatologist. Dermatologists are health professionals primarily focused on diagnosing conditions associated with the skin, hair, and nails. This doctor treats various skin disorders, namely acne, skin cancer, and over 3000 skin conditions. Aside from that, they could also provide several treatments that deal with everything from acne to anti-aging procedures.
Dermatologist. Dermatologists are health professionals primarily focused on diagnosing conditions associated with the skin, hair, and nails. This doctor treats various skin disorders, namely acne, skin cancer, and over 3000 skin conditions. Aside from that, they could also provide several treatments that deal with everything from acne to anti-aging procedures.  How to become a Dermatologist?
How to become a Dermatologist?
> - Dietitian/Dietician
 Dietitian/Dietician. A dietitian is a specialist in human nutrition and the regulation of diet, also known as dietetics. A dietitian recommends nutrition based on the patient’s medical conditions (such as eating disorders) and individual needs. Aspiring students who want to become a dietitian should complete medical degrees and obtain licenses to assess, diagnose, and treat nutritional malfunctions .
Dietitian/Dietician. A dietitian is a specialist in human nutrition and the regulation of diet, also known as dietetics. A dietitian recommends nutrition based on the patient’s medical conditions (such as eating disorders) and individual needs. Aspiring students who want to become a dietitian should complete medical degrees and obtain licenses to assess, diagnose, and treat nutritional malfunctions . Best Colleges for Nutrition and Dietetics ?
Best Colleges for Nutrition and Dietetics ?
> - Emergency Room (ER) Doctor
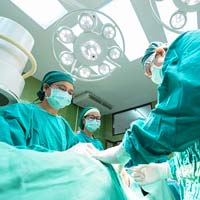 Emergency Room (ER) Doctor. Emergency doctors care for patients with immediate medical attention such as acute illnesses or injuries from accidents, and they would undertake acute interventions to stabilize the patient. The emergency physician is a professional in high-level cardiac life support techniques such as resuscitation, vital signs, trauma care in fractures and soft tissue injuries, and supervision of other life-threatening conditions .
Emergency Room (ER) Doctor. Emergency doctors care for patients with immediate medical attention such as acute illnesses or injuries from accidents, and they would undertake acute interventions to stabilize the patient. The emergency physician is a professional in high-level cardiac life support techniques such as resuscitation, vital signs, trauma care in fractures and soft tissue injuries, and supervision of other life-threatening conditions . How to become an ER doctor?
How to become an ER doctor?
> - Endocrinologist
 Endocrinologist. An endocrinologist is a medical doctor under the internal medicine category who studies the diseases that affect the endocrine system, which is responsible for secreting and regulating the body’s hormone levels. Reproductive Endocrinologist treats both women and men with infertility issues. Suggested Reading: Top 25 Endocrine System Fun Facts
Endocrinologist. An endocrinologist is a medical doctor under the internal medicine category who studies the diseases that affect the endocrine system, which is responsible for secreting and regulating the body’s hormone levels. Reproductive Endocrinologist treats both women and men with infertility issues. Suggested Reading: Top 25 Endocrine System Fun Facts  How to become an Endocrinologist?
How to become an Endocrinologist?
> - Epidemiologist
 Epidemiologist. An epidemiologist studies the causes and patterns of diseases in a population or area and tries to prevent epidemics/pandemics from reoccurring. They are more scientists than doctors who specialize in the highly viral epidemic illness (such as new diseases) and provide or develop cures and also modes of prevention of diseases with vaccinations .
Epidemiologist. An epidemiologist studies the causes and patterns of diseases in a population or area and tries to prevent epidemics/pandemics from reoccurring. They are more scientists than doctors who specialize in the highly viral epidemic illness (such as new diseases) and provide or develop cures and also modes of prevention of diseases with vaccinations . How to become an Epidemiologist?
How to become an Epidemiologist?
> - Family Medicine Physician
 Family Medicine Physician. Family physicians specializing in family medicine are knowledgeable and can treat various medical diseases of patients of all ages. These doctors provide preventive care for patients, which includes annual checkups, periodic immunizations, contraception, and allergy medications. A physician specialized in this field is a pediatrician and an internist combined into one. They also referred as hospitalists.
Family Medicine Physician. Family physicians specializing in family medicine are knowledgeable and can treat various medical diseases of patients of all ages. These doctors provide preventive care for patients, which includes annual checkups, periodic immunizations, contraception, and allergy medications. A physician specialized in this field is a pediatrician and an internist combined into one. They also referred as hospitalists.  How to become a Family Medicine Physician?
How to become a Family Medicine Physician?
> - Gastroenterologist
 Gastroenterologist As their name suggests, gastroenterologists are medical professionals focused on the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal (digestive system) tract which includes the stomach, small and large intestines, pancreas, and liver. Gastroenterologists also perform a variety of procedures in colonoscopy, endoscopy, ERCP, endoscopic ultrasound, and liver-biopsy as well.
Gastroenterologist As their name suggests, gastroenterologists are medical professionals focused on the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal (digestive system) tract which includes the stomach, small and large intestines, pancreas, and liver. Gastroenterologists also perform a variety of procedures in colonoscopy, endoscopy, ERCP, endoscopic ultrasound, and liver-biopsy as well.  How to become a Gastroenterologist?
How to become a Gastroenterologist?
> - Geriatrician
 Geriatrician. A Geriatrician takes care of older adults. Because of their declining immunity that arises with senility and their multiple health complications, older adults need to be highly taken care of. The main difference between geriatrics, the care of aged people, and gerontology is the study of the aging process. There are different types of geriatricians within Geriatrics based on the diseases in elders.
Geriatrician. A Geriatrician takes care of older adults. Because of their declining immunity that arises with senility and their multiple health complications, older adults need to be highly taken care of. The main difference between geriatrics, the care of aged people, and gerontology is the study of the aging process. There are different types of geriatricians within Geriatrics based on the diseases in elders.  How to become a Geriatrician?
How to become a Geriatrician?
> - Hyperbaric Physician
 Hyperbaric Physician. Hyperbaric physicians/doctors are medical doctors trained in hyperbaric medicine, such as providing hyperbaric Oxygen (HBO – higher pressure of Oxygen than what we see in the air around us) therapy for conditions such as decompression illness and carbon monoxide poisoning from fire fumes. Hyperbaric medicine covers hyperbaric oxygen treatment, which is at the atmospheric pressure to increase the oxygen flow in the body.
Hyperbaric Physician. Hyperbaric physicians/doctors are medical doctors trained in hyperbaric medicine, such as providing hyperbaric Oxygen (HBO – higher pressure of Oxygen than what we see in the air around us) therapy for conditions such as decompression illness and carbon monoxide poisoning from fire fumes. Hyperbaric medicine covers hyperbaric oxygen treatment, which is at the atmospheric pressure to increase the oxygen flow in the body.  How to become a Hyperbaric Physician?
How to become a Hyperbaric Physician?
> - Hematologist
 Hematologist. A hematologist is a specialist in hematology, which is the study of blood, blood-forming organs, and blood-related diseases (sickle cell).Typical hematologist treats blood disorders and malignancies, including hemophilia, leukemia, lymphoma, and sickle-cell anemia.
Hematologist. A hematologist is a specialist in hematology, which is the study of blood, blood-forming organs, and blood-related diseases (sickle cell).Typical hematologist treats blood disorders and malignancies, including hemophilia, leukemia, lymphoma, and sickle-cell anemia.  How to become a Hematologist?
How to become a Hematologist?
> - Hepatologist
 Hepatologist. A hepatologist is a specialized doctor who studies, prevents, diagnoses, and manages diseases that affect the liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas. The term hepatology is derived from the Greek words “hepatikos” meaning liver and “logia“, meaning study. Transplant Hepatologists are gastroenterologists or hepatologists who specialize in the management of patients with advanced liver disease, particularly those requiring liver transplantation. They evaluate patients for transplant eligibility, manage pre-and post-transplant care, and collaborate with transplant surgeons and other healthcare professionals involved in the transplant process.
Hepatologist. A hepatologist is a specialized doctor who studies, prevents, diagnoses, and manages diseases that affect the liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas. The term hepatology is derived from the Greek words “hepatikos” meaning liver and “logia“, meaning study. Transplant Hepatologists are gastroenterologists or hepatologists who specialize in the management of patients with advanced liver disease, particularly those requiring liver transplantation. They evaluate patients for transplant eligibility, manage pre-and post-transplant care, and collaborate with transplant surgeons and other healthcare professionals involved in the transplant process.  How to become a Hepatologist?
How to become a Hepatologist?
> - Immunologist
 Immunologist. An immunologist is a medical professional who investigates and studies the physiological processes and functions of the body’s immune system. This knowledge is then applied in the diagnosis and treatment of a range of diseases that affect the said system.
Immunologist. An immunologist is a medical professional who investigates and studies the physiological processes and functions of the body’s immune system. This knowledge is then applied in the diagnosis and treatment of a range of diseases that affect the said system.  How to become an Immunologist?
How to become an Immunologist?
> - Infectious Disease Specialist
 Infectious Disease Specialist. Infectious disease specialist (medical doctor) who treats and diagnoses complex infections such as HIV or TB. The infectious disease specialist can perform their services in hospitals or may be out-patient based. Check out the top 15 deadliest bacterial diseases here.
Infectious Disease Specialist. Infectious disease specialist (medical doctor) who treats and diagnoses complex infections such as HIV or TB. The infectious disease specialist can perform their services in hospitals or may be out-patient based. Check out the top 15 deadliest bacterial diseases here.  How to become an Infectious
How to become an Infectious
Disease Specialist?
> - Intensivist
 Intensivist. An intensivist is a medical doctor specializing in training and treating critically ill patients in ICU (Intensive Care Unit). Intensivists can be internal medicine specialists (often pulmonologists), anesthesiologists, ER doctors, pediatricians, or surgeons. They are also referred as a critical care physician or critical care medicine specialist.
Intensivist. An intensivist is a medical doctor specializing in training and treating critically ill patients in ICU (Intensive Care Unit). Intensivists can be internal medicine specialists (often pulmonologists), anesthesiologists, ER doctors, pediatricians, or surgeons. They are also referred as a critical care physician or critical care medicine specialist.  How to become an Intensivist?
How to become an Intensivist?
> - Internal Medicine Specialist
 Internal Medicine Specialist. An Internal Medicine Specialist, an internist, specializes in managing and treating chronic adult illnesses through non-surgical procedures like pain relievers and anesthetics. Internists usually have sub-branches in diseases concerning particular organs or organ systems. They mostly work in hospitals to render their services.
Internal Medicine Specialist. An Internal Medicine Specialist, an internist, specializes in managing and treating chronic adult illnesses through non-surgical procedures like pain relievers and anesthetics. Internists usually have sub-branches in diseases concerning particular organs or organ systems. They mostly work in hospitals to render their services.  How to become an Internal Medicine Specialist?
How to become an Internal Medicine Specialist?
> - Maxillofacial Surgeon / Oral Surgeon
 Maxillofacial Surgeon / Oral Surgeon. Maxillofacial Surgeons are dentists trained in performing surgery on the mouth and jaw. Maxillofacial surgeons specialize in treating and reconstructing areas of the face, head, or neck after an injury or surgery. The surgeries include Dentoalveolar surgery, bone-fused dental implants, cosmetic surgery of the head and neck, and corrective jaw surgery.
Maxillofacial Surgeon / Oral Surgeon. Maxillofacial Surgeons are dentists trained in performing surgery on the mouth and jaw. Maxillofacial surgeons specialize in treating and reconstructing areas of the face, head, or neck after an injury or surgery. The surgeries include Dentoalveolar surgery, bone-fused dental implants, cosmetic surgery of the head and neck, and corrective jaw surgery.  How to become an Oral Surgeon?
How to become an Oral Surgeon?
> - Medical Examiner
 Medical Examiner. A medical examiner is a publicly appointed government doctor specializing in forensic pathology and autopsies. The medical examiner reviews deaths defined by regulations and local laws, essential for public health and welfare. These medical examiners review the autopsy reports to assess the exact cause of the death other than natural causes such as sudden and unexpected deaths.
Medical Examiner. A medical examiner is a publicly appointed government doctor specializing in forensic pathology and autopsies. The medical examiner reviews deaths defined by regulations and local laws, essential for public health and welfare. These medical examiners review the autopsy reports to assess the exact cause of the death other than natural causes such as sudden and unexpected deaths.  How to become a Medical Examiner?
How to become a Medical Examiner?
> - Medical Geneticist
 Medical Geneticist. A medical geneticist is trained in general medicine, genetic diagnosis, and treating patients with genetic disorders. They use molecular genetics, cytogenetics, and biochemical tests to treat patients with a comprehensive molecular and clinical approach. Check out the genetic testing pros and cons here.
Medical Geneticist. A medical geneticist is trained in general medicine, genetic diagnosis, and treating patients with genetic disorders. They use molecular genetics, cytogenetics, and biochemical tests to treat patients with a comprehensive molecular and clinical approach. Check out the genetic testing pros and cons here.  How to become a Medical Geneticist?
How to become a Medical Geneticist?
> - Medical Toxicologist
 Medical Toxicologist. Medical Toxicologists specialize in the diagnosis, management, and prevention of poisoning and other adverse health effects caused by medications, occupational and environmental toxins, and biological agents. They treat patients with acute or chronic poisoning and provide guidance on poison prevention, substance abuse, and hazardous materials. To become a Medical Toxicologist, one must complete medical school (MD or DO), followed by a residency in emergency medicine, pediatrics, or another primary specialty, and then a fellowship in medical toxicology. Board certification is available through the American Board of Medical Toxicology or the American Board of Emergency Medicine.
Medical Toxicologist. Medical Toxicologists specialize in the diagnosis, management, and prevention of poisoning and other adverse health effects caused by medications, occupational and environmental toxins, and biological agents. They treat patients with acute or chronic poisoning and provide guidance on poison prevention, substance abuse, and hazardous materials. To become a Medical Toxicologist, one must complete medical school (MD or DO), followed by a residency in emergency medicine, pediatrics, or another primary specialty, and then a fellowship in medical toxicology. Board certification is available through the American Board of Medical Toxicology or the American Board of Emergency Medicine.
How to become a Medical Toxicologist?
> - Neonatologist
 Neonatologist, A neonatologist is a type of pediatrician specializing in the medical care of infants, particularly critically ill premature and full-time infants. Also, neonatologists work as general pediatricians providing care to ICU-borne newborn babies who require critical and urgent care. Some neonatologists, particularly those in educational settings, may monitor babies for months or sometimes years after hospital discharge to better evaluate the long-term effects of health problems early in life.
Neonatologist, A neonatologist is a type of pediatrician specializing in the medical care of infants, particularly critically ill premature and full-time infants. Also, neonatologists work as general pediatricians providing care to ICU-borne newborn babies who require critical and urgent care. Some neonatologists, particularly those in educational settings, may monitor babies for months or sometimes years after hospital discharge to better evaluate the long-term effects of health problems early in life.  How to become a Neonatologist?
How to become a Neonatologist?
> - Nephrologist
 Nephrologist. Nephrologists are trained medical doctors in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the kidney and urinary systems, such as inflammation of the kidneys, kidney biopsy, dialysis, chronic kidney disease, or cancer. For kids, pediatric nephrologists only treat children.
Nephrologist. Nephrologists are trained medical doctors in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the kidney and urinary systems, such as inflammation of the kidneys, kidney biopsy, dialysis, chronic kidney disease, or cancer. For kids, pediatric nephrologists only treat children.  How to become a Nephrologist?
How to become a Nephrologist?
> - Neurologist
 Neurologist. A neurologist is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of the diseases that affect the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, and the neurons).Neurologists treat Demyelinating diseases (i.e., multiple sclerosis), Cerebrovascular diseases (i.e., stroke), Headache disorders, and infections of the brain.
Neurologist. A neurologist is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of the diseases that affect the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, and the neurons).Neurologists treat Demyelinating diseases (i.e., multiple sclerosis), Cerebrovascular diseases (i.e., stroke), Headache disorders, and infections of the brain.  How to become a Neurologist?
How to become a Neurologist?
> - Neurosurgeon
 Neurosurgeon. Although they also deal with diagnosing and treating nervous system diseases like what neurologists do, neurosurgeons are licensed to operate and perform surgeries on the patient’s brain. There are several sub-branches of neurosurgery, namely: Vascular neurosurgery, Stereotactic Neurosurgery, Skull base surgery, Spinal neurosurgery, Peripheral nerve surgery, Oncological neurosurgery, and Pediatric Neurosurgery. Suggested Reading: Best Neurosurgery Schools in the US.
Neurosurgeon. Although they also deal with diagnosing and treating nervous system diseases like what neurologists do, neurosurgeons are licensed to operate and perform surgeries on the patient’s brain. There are several sub-branches of neurosurgery, namely: Vascular neurosurgery, Stereotactic Neurosurgery, Skull base surgery, Spinal neurosurgery, Peripheral nerve surgery, Oncological neurosurgery, and Pediatric Neurosurgery. Suggested Reading: Best Neurosurgery Schools in the US.  How to become a Neurosurgeon?
How to become a Neurosurgeon?
> - Nuclear Medicine Specialist
 Nuclear Medicine Specialist. Nuclear medicine specialists are trained medical doctors who administer radioactive medicines to diagnose and treat specific conditions, including bone scans, lung perfusion scans, & HIDA scans for gallbladder function. The common procedures in nuclear medicine based on the medical conditions include brain perfusion & glucose metabolic imaging, blood pool imaging, gastric emptying studies, hepatobiliary imaging, lymphoscintigraphy, parathyroid imaging, pulmonary perfusion & ventilation imaging, renal function imaging, thyroid imaging, thyroid whole body imaging, urinary tract imaging, and white blood cell studies.
Nuclear Medicine Specialist. Nuclear medicine specialists are trained medical doctors who administer radioactive medicines to diagnose and treat specific conditions, including bone scans, lung perfusion scans, & HIDA scans for gallbladder function. The common procedures in nuclear medicine based on the medical conditions include brain perfusion & glucose metabolic imaging, blood pool imaging, gastric emptying studies, hepatobiliary imaging, lymphoscintigraphy, parathyroid imaging, pulmonary perfusion & ventilation imaging, renal function imaging, thyroid imaging, thyroid whole body imaging, urinary tract imaging, and white blood cell studies.  How to become a Nuclear Medicine Specialist?
How to become a Nuclear Medicine Specialist?
> - Obstetrician/Gynecologist (OB/GYN)
 Obstetrician/Gynecologist (OB/GYN). Commonly abbreviated as OB/GYN, an obstetrician/gynecologist combines two doctors. An obstetrician is a doctor trained to manage pregnancy, labor, and childbirth. On the other hand, a gynecologist is a doctor who specializes in the female reproductive system.
Obstetrician/Gynecologist (OB/GYN). Commonly abbreviated as OB/GYN, an obstetrician/gynecologist combines two doctors. An obstetrician is a doctor trained to manage pregnancy, labor, and childbirth. On the other hand, a gynecologist is a doctor who specializes in the female reproductive system.
Primatologist is a specialized doctor within OBGYN who treats patients with high-risk pregnancies. Gynecologic oncologists are medical specialists who treat and diagnose women who have cancers in reproductive organs such as the ovaries and uterus. How to become an OB/GYN?
How to become an OB/GYN?
> - Occupational Medicine Specialist
 Occupational Medicine Specialist. An occupational medicine (OM) specialist is a medical doctor trained to provide continuous care for injured workers and help them return to work. They also support organizations to maintain a safe and healthy workplace (Occupational medicine).OM physicians work to ensure that the highest occupational health and safety standards are accomplished and kept in the workplace. Also, OM specialists are involved in other disciplines, such as preventing illness (such as flu by administering the flu shots), injury, and disability at the workplace.
Occupational Medicine Specialist. An occupational medicine (OM) specialist is a medical doctor trained to provide continuous care for injured workers and help them return to work. They also support organizations to maintain a safe and healthy workplace (Occupational medicine).OM physicians work to ensure that the highest occupational health and safety standards are accomplished and kept in the workplace. Also, OM specialists are involved in other disciplines, such as preventing illness (such as flu by administering the flu shots), injury, and disability at the workplace.  How to become an OM Specialist?
How to become an OM Specialist?
> - Oncologist
 Oncologist. Coming from the Greek word “onkos” which means “tumor” or “mass“, oncology is the branch of science that deals with cancers. Hence, oncologists are medical doctors who specialize in diagnosing, preventing, and treating cancer. There are different types of physicians within the Oncologist profession, namely: medical oncologist (chemotherapy or medications), a surgical oncologist (surgical procedure of a variety of tumors), radiation oncologist (megavoltage X-rays or radionuclides) and pediatric oncologist (physician specializing in childhood cancer).
Oncologist. Coming from the Greek word “onkos” which means “tumor” or “mass“, oncology is the branch of science that deals with cancers. Hence, oncologists are medical doctors who specialize in diagnosing, preventing, and treating cancer. There are different types of physicians within the Oncologist profession, namely: medical oncologist (chemotherapy or medications), a surgical oncologist (surgical procedure of a variety of tumors), radiation oncologist (megavoltage X-rays or radionuclides) and pediatric oncologist (physician specializing in childhood cancer). How to become an Oncologist?
How to become an Oncologist?
> - Ophthalmologist
 Ophthalmologist. Unlike optometrists, who are also “eye doctors”, ophthalmologists can perform surgeries on the eyes. Moreover, they are considered medical and surgical specialists because they can perform operations on the eyes. Ophthalmologists diagnose various eye-related diseases such as Cataracts, Glaucoma, Macular degeneration, Diabetic retinopathy, dry eyes, Strabismus, Proptosis, Uveitis, Eye tumors, Refractive surgery, and more. Ophthalmology has subspecialties to specialize in particular eye diseases.
Ophthalmologist. Unlike optometrists, who are also “eye doctors”, ophthalmologists can perform surgeries on the eyes. Moreover, they are considered medical and surgical specialists because they can perform operations on the eyes. Ophthalmologists diagnose various eye-related diseases such as Cataracts, Glaucoma, Macular degeneration, Diabetic retinopathy, dry eyes, Strabismus, Proptosis, Uveitis, Eye tumors, Refractive surgery, and more. Ophthalmology has subspecialties to specialize in particular eye diseases.  How to become an Ophthalmologist?
How to become an Ophthalmologist? How to become an Optometrist?
How to become an Optometrist? How to become an Orthoptist?
How to become an Orthoptist? How to become an Optician?
How to become an Optician?
> - Orthopedic Surgeon / Orthopedist
 Orthopedic Surgeon / Orthopedist. Orthopedic surgeons (aka Orthopedist) are doctors specially trained to diagnose and treat. They operate on patients with diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system (which includes the muscles, broken bones, ligaments, tendons, and the nerves).Hand surgeons specialize in performing surgery for hand-related injuries and complications.
Orthopedic Surgeon / Orthopedist. Orthopedic surgeons (aka Orthopedist) are doctors specially trained to diagnose and treat. They operate on patients with diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system (which includes the muscles, broken bones, ligaments, tendons, and the nerves).Hand surgeons specialize in performing surgery for hand-related injuries and complications.  How to become an Orthopedic Surgeon?
How to become an Orthopedic Surgeon?
> - Otolaryngologist (aka ENT Specialist)
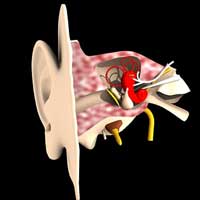 Otolaryngologist (aka ENT Specialist). An otolaryngologist is a type of physician who specializes in managing and treating patients with various disorders of the Ear, Nose, and Throat. In addition to that, they also diagnose diseases that affect related structures like the head and neck. There are subspecialties within Otolaryngology that specialize in particular ENT regions, which include Head & Neck oncologic surgery, facial plastic and reconstructive surgery, otology-neurotology, rhinology & sinus surgery, laryngology & voice-related disorders, pediatric otorhinolaryngology, and sleep medicine.
Otolaryngologist (aka ENT Specialist). An otolaryngologist is a type of physician who specializes in managing and treating patients with various disorders of the Ear, Nose, and Throat. In addition to that, they also diagnose diseases that affect related structures like the head and neck. There are subspecialties within Otolaryngology that specialize in particular ENT regions, which include Head & Neck oncologic surgery, facial plastic and reconstructive surgery, otology-neurotology, rhinology & sinus surgery, laryngology & voice-related disorders, pediatric otorhinolaryngology, and sleep medicine.  How to become an Otolaryngologist (aka ENT doctor)?
How to become an Otolaryngologist (aka ENT doctor)?
> - Osteopath
 Osteopath. An osteopath (aka osteopathic physician) is a medical doctor who specializes in osteopathic medicine. Osteopath strives to improve people’s overall health and wellness by treating the whole person rather than a condition or disease they may have. An osteopath can prescribe osteopathic manipulative medications and focus on stretching, massaging, and moving the musculoskeletal system to reduce pain and improve mobility, circulation of blood and lymphatic fluids.
Osteopath. An osteopath (aka osteopathic physician) is a medical doctor who specializes in osteopathic medicine. Osteopath strives to improve people’s overall health and wellness by treating the whole person rather than a condition or disease they may have. An osteopath can prescribe osteopathic manipulative medications and focus on stretching, massaging, and moving the musculoskeletal system to reduce pain and improve mobility, circulation of blood and lymphatic fluids.
How to become an Osteophathic Physician (Osteopath)
> - Palliative Care Specialist
 Palliative Care Specialist. Palliative medicine is a sub-specialty of internal medicine that relieves suffering and improves the quality of life for patients with chronic, curable, or life-threatening diseases. Physicians are sometimes called palliative care specialists by rendering palliative therapies without curative intent (i.e., when no cure can be expected – as often happens in late-stage cancers).Medicines and therapies are considered palliative if they relieve symptoms without healing the underlying disease or cause (e.g., treating chemotherapy-related nausea and providing painkillers).
Palliative Care Specialist. Palliative medicine is a sub-specialty of internal medicine that relieves suffering and improves the quality of life for patients with chronic, curable, or life-threatening diseases. Physicians are sometimes called palliative care specialists by rendering palliative therapies without curative intent (i.e., when no cure can be expected – as often happens in late-stage cancers).Medicines and therapies are considered palliative if they relieve symptoms without healing the underlying disease or cause (e.g., treating chemotherapy-related nausea and providing painkillers).
How to become a Palliative Care Specialist?
> - Parasitologist
 Parasitologist. Parasitologists deal with parasites (microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, worms, and insects) that could either live temporarily or permanently, on or inside the human body. Parasitologists use techniques learned from cell biology, bioinformatics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, genetics, evolution & even ecology. Also with parasitology, there are subdisciplines such as medical/human parasitologists who study parasites in humans; Veterinary parasitologists who study parasites on cattle and pets (animals).
Parasitologist. Parasitologists deal with parasites (microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, worms, and insects) that could either live temporarily or permanently, on or inside the human body. Parasitologists use techniques learned from cell biology, bioinformatics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, genetics, evolution & even ecology. Also with parasitology, there are subdisciplines such as medical/human parasitologists who study parasites in humans; Veterinary parasitologists who study parasites on cattle and pets (animals). How to become a Parasitologist?
How to become a Parasitologist?
> - Pathologist
 Pathologist. A pathologist is a trained medical doctor who performs autopsies in examining tissue (such as a mole) and blood samples to diagnose a disease and produce a pathological report. A pale pathologist is a doctor that studies ancient diseases. A forensic pathologist is a medical doctor who performs autopsies to find the cause of death when the crime is involved in the scene.
Pathologist. A pathologist is a trained medical doctor who performs autopsies in examining tissue (such as a mole) and blood samples to diagnose a disease and produce a pathological report. A pale pathologist is a doctor that studies ancient diseases. A forensic pathologist is a medical doctor who performs autopsies to find the cause of death when the crime is involved in the scene.- Anatomic Pathologists concentrate on scrutinizing tissues and organs to diagnose disorders. These professionals examine biopsies, surgical specimens, and autopsies to recognize anomalies and offer vital information for patient care and treatment. They work closely with other physicians and medical experts to guide treatment decisions.Clinical Pathologists specialize in the analysis of body fluids, such as blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid, to diagnose and monitor diseases. They oversee laboratories, ensuring accurate testing and reporting of results, which are vital for patient care and treatment decisions. They also collaborate with other medical professionals to provide comprehensive care.Cytopathologists specialize in diagnosing diseases by examining individual cells obtained from body fluids, scrapings, or fine needle aspirations. They are essential in cancer diagnosis and management, especially in identifying malignancies and determining their origin. They may also identify infections and inflammatory processes. They collaborate with other medical professionals and contribute to research in their field.Dermatopathologists possess a specific interest in identifying skin diseases, including dermal cancers, by scrutinizing tissue samples under the magnifying instrument. They work with dermatologists and other experts to determine the most fitting treatment blueprint for patients. Moreover, they contribute to dermatology and dermatopathology research and education.Hematopathologists hold expertise in identifying blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic system ailments by examining blood, bone marrow, and tissue samples under the magnifying instrument. They are pivotal in detecting and handling hematologic tumors like leukemia, lymphoma, and non-malignant blood disorders. These specialists collaborate with oncologists, hematologists, and other experts to formulate treatment methodologies and provide their contributions toward research in their respective domains.Molecular Pathologists employ sophisticated molecular and genetic methodologies to diagnose illnesses, foretell disease advancement, and recognize specific therapies. They are crucial in personalized medication by directing and selecting apt treatments, particularly for cancer patients. These specialists work with other healthcare experts and contribute to molecular pathology research and education.
 How to become a Pathologist?
How to become a Pathologist?
> - Perinatologist
 Perinatologist. A Perinatologist is a specialized doctor who cares for the fetus and complicated, high-risk pregnancies. Perinatology is sometimes referred to as maternal-fetal medicine. These types of doctors take special care of pregnant women who have chronic medical conditions such as heart diseases, blood pressure (hypertension), diabetes, or thrombophilia).They will help them with pregnancy-related complications such as preterm labor, twin/triplet pregnancies, pre-eclampsia, and so on).
Perinatologist. A Perinatologist is a specialized doctor who cares for the fetus and complicated, high-risk pregnancies. Perinatology is sometimes referred to as maternal-fetal medicine. These types of doctors take special care of pregnant women who have chronic medical conditions such as heart diseases, blood pressure (hypertension), diabetes, or thrombophilia).They will help them with pregnancy-related complications such as preterm labor, twin/triplet pregnancies, pre-eclampsia, and so on). How to become a Perinatologist?
How to become a Perinatologist?
> - Periodontist
 Periodontist. A periodontist is a board-certified doctor specializing in oral health care. Also, a periodontist can even diagnose and treat periodontal disease (gum disease) and is involved in the placement of dental implants. Periodontal diseases include P. gingivalis, T. forsythia, and T. denticola. Untreated may lead to alveolar bone loss and tooth loss. One must complete a dental degree before applying for the postgraduate training program in periodontology.
Periodontist. A periodontist is a board-certified doctor specializing in oral health care. Also, a periodontist can even diagnose and treat periodontal disease (gum disease) and is involved in the placement of dental implants. Periodontal diseases include P. gingivalis, T. forsythia, and T. denticola. Untreated may lead to alveolar bone loss and tooth loss. One must complete a dental degree before applying for the postgraduate training program in periodontology.  How to become a Periodontist?
How to become a Periodontist?
> - Pediatrician
 Pediatrician. A pediatrician is involved in managing the physical, emotional and, behavioral, & mental health of their young patients. Pediatricians focus on infants, children, teenagers, and young adults (up to 21 years old).The pediatricians who treat teenagers sometimes referred as Adolescent medicine specialist. A developmental pediatrician specializes in treating children with disabilities such as autism, cerebral palsy, down-syndrome, ADHD, and behavioral disorders.
Pediatrician. A pediatrician is involved in managing the physical, emotional and, behavioral, & mental health of their young patients. Pediatricians focus on infants, children, teenagers, and young adults (up to 21 years old).The pediatricians who treat teenagers sometimes referred as Adolescent medicine specialist. A developmental pediatrician specializes in treating children with disabilities such as autism, cerebral palsy, down-syndrome, ADHD, and behavioral disorders.  How to become a Pediatrician?
How to become a Pediatrician?
> - Preventive Medicine Specialist
 Preventive Medicine Specialist. Preventive Medical Practitioners primarily emphasize advancing physical and mental wellness, as well as impeding illness, handicap, and untimely mortality. These specialists labor in diverse environments such as public health establishments, governmental organizations, and clinical settings. Their obligations include formulating and executing preventive strategies, conducting in-depth research, and offering counsel on public health regulations. To become a Preventive Medicine Specialist, one must complete medical school (MD or DO), followed by a residency in preventive medicine or another primary specialty, and then a fellowship in a related field, if desired. Board certification is available through the American Board of Preventive Medicine. How to become a Preventive Medicine Specialist?
Preventive Medicine Specialist. Preventive Medical Practitioners primarily emphasize advancing physical and mental wellness, as well as impeding illness, handicap, and untimely mortality. These specialists labor in diverse environments such as public health establishments, governmental organizations, and clinical settings. Their obligations include formulating and executing preventive strategies, conducting in-depth research, and offering counsel on public health regulations. To become a Preventive Medicine Specialist, one must complete medical school (MD or DO), followed by a residency in preventive medicine or another primary specialty, and then a fellowship in a related field, if desired. Board certification is available through the American Board of Preventive Medicine. How to become a Preventive Medicine Specialist?
> - Physiatrist
 Physiatrist. A physiatrist is a medical physician helping patients recover after trauma such as a stroke or surgery. In treating these patients, physiatrists lead a group of physical, occupational, recreational, and speech therapists, nurses, psychologists (for counseling), and other social workers to help with faster recovery. Note that physical medicine and rehabilitation (PMR), also referred to as physiatry or rehabilitation medicine, targets to improve and restore functional ability and quality of life for patients with physical impairments affecting the critical organs namely brain, spinal cord, nerves, bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, and tendons. The other subspecialties of physiatrists include neuromuscular medicine, pain medications, pediatric rehabilitation medicine, spinal cord injury, sports medicine, brain injury (stroke), and palliative medicine.
Physiatrist. A physiatrist is a medical physician helping patients recover after trauma such as a stroke or surgery. In treating these patients, physiatrists lead a group of physical, occupational, recreational, and speech therapists, nurses, psychologists (for counseling), and other social workers to help with faster recovery. Note that physical medicine and rehabilitation (PMR), also referred to as physiatry or rehabilitation medicine, targets to improve and restore functional ability and quality of life for patients with physical impairments affecting the critical organs namely brain, spinal cord, nerves, bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, and tendons. The other subspecialties of physiatrists include neuromuscular medicine, pain medications, pediatric rehabilitation medicine, spinal cord injury, sports medicine, brain injury (stroke), and palliative medicine.  How to become a Physiatrist?
How to become a Physiatrist?
> - Plastic Surgeon
 Plastic Surgeon. Plastic surgeons are specialized medical doctors in surgery that improve a person’s outlook, such as surgery for a congenital disability (e.g., cleft palate), or surgery following an injury or the removal of cancer, such as breast implant surgery after breast removal (mastectomy).The sub-specialties of plastic surgery include Aesthetic surgery (cosmetics), burn surgery (fire wounds), Craniofacial surgery (congenital anomalies), hand surgery (congenital malformations), microsurgery (breast reconstruction), and Pediatric plastic surgery (congenital disability corrections).
Plastic Surgeon. Plastic surgeons are specialized medical doctors in surgery that improve a person’s outlook, such as surgery for a congenital disability (e.g., cleft palate), or surgery following an injury or the removal of cancer, such as breast implant surgery after breast removal (mastectomy).The sub-specialties of plastic surgery include Aesthetic surgery (cosmetics), burn surgery (fire wounds), Craniofacial surgery (congenital anomalies), hand surgery (congenital malformations), microsurgery (breast reconstruction), and Pediatric plastic surgery (congenital disability corrections). How to become a Plastic Surgeon?
How to become a Plastic Surgeon?
> - Psychiatrist
 Psychiatrist. Psychiatrists spend most of their time providing medical treatments to mental-disorder patients. These patients have problems with their thoughts, emotions, or behavior (conditions from depression to Schizophrenia to Delirium to ADHD). Psychiatrists provide treatments using physical treatments (medicines) or psychological treatments (therapy), and social treatments. There are many different types of a psychiatrist:
Psychiatrist. Psychiatrists spend most of their time providing medical treatments to mental-disorder patients. These patients have problems with their thoughts, emotions, or behavior (conditions from depression to Schizophrenia to Delirium to ADHD). Psychiatrists provide treatments using physical treatments (medicines) or psychological treatments (therapy), and social treatments. There are many different types of a psychiatrist:- Addiction Psychiatrists: They look after patients who have drug or behavioral addictions (such as gambling and alcoholism).Child and Adolescent Psychiatrists: They care for younger people and their particular mental health concerns (such as ADHD, Autism, and Childhood Anxiety).Geriatric Psychiatrists (or Psychogeriatricians): They look after the elderly (issues such as hoarding, dementia, grief, and loss).Forensic Psychiatrists: They assess and care for prisoners and people accused of crimes and have a role in advising courts about how mental illness can affect criminal behavior.Psychosomatic Medicine is a branch of psychiatry that deals with the relationships between physical and mental illness (such as in Delirium).Consultation-Liaison Psychiatrists: They are also known as Psychosomatic Medicine Practitioners, who work with patients with both psychiatric and medical issues, providing psychiatric consultations in hospital settings. They collaborate with other medical specialists to address the psychiatric aspects of patients’ conditions, such as managing delirium, anxiety, or depression related to medical illness or surgery. They also contribute to research and education in consultation-liaison psychiatry.
 How to become a Psychiatrist?
How to become a Psychiatrist?
> - Pulmonologist
 Pulmonologist. A pulmonologist specializes in pulmonary (lungs) and other respiratory tract illnesses and diseases. These different types of doctors have a broad scope of specialization as they can treat almost everything from asthma to tuberculosis.
Pulmonologist. A pulmonologist specializes in pulmonary (lungs) and other respiratory tract illnesses and diseases. These different types of doctors have a broad scope of specialization as they can treat almost everything from asthma to tuberculosis.  How to become a Pulmonologist?
How to become a Pulmonologist?
> - Radiologist
 Radiologist. A radiologist is a medical professional trained to diagnose and treat patients by interpreting test results from medical imaging techniques. Such techniques include X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scan, and positron emission tomography (PET).
Radiologist. A radiologist is a medical professional trained to diagnose and treat patients by interpreting test results from medical imaging techniques. Such techniques include X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scan, and positron emission tomography (PET). How to become a Radiologist?
How to become a Radiologist?
> - Rheumatologist
 Rheumatologist. A rheumatologist is an MD who practices in the field of medical sub-specialty named rheumatology, which deals with the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases such as back pain, Bursitis/Tendinitis, Capsulitis, neck pain, Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and also immune-mediated disorders (e.g., connective tissue diseases, soft-tissue rheumatism, and autoimmune diseases).
Rheumatologist. A rheumatologist is an MD who practices in the field of medical sub-specialty named rheumatology, which deals with the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases such as back pain, Bursitis/Tendinitis, Capsulitis, neck pain, Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and also immune-mediated disorders (e.g., connective tissue diseases, soft-tissue rheumatism, and autoimmune diseases). How to become a Rheumatologist?
How to become a Rheumatologist?
> - Sleep Disorders Specialist
 Sleep Doctor / Sleep Disorders Specialist. A sleep doctor is a medical doctor specializing in the diagnosis & treatment of sleep-related disorders such as Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA).There are three types of sleep apnea, namely obstructive (OSA), central (CSA), and a mixture of the two called mixed sleep apnea. Risk factors for OSA result in overweight, allergies, a small airway, and enlarged tonsils. Sleep doctor also treats other sleep-related disorders, namely insomnia, Restless legs syndrome, Periodic leg movement disorder, Narcolepsy, Circadian rhythm disorder, and a few more.
Sleep Doctor / Sleep Disorders Specialist. A sleep doctor is a medical doctor specializing in the diagnosis & treatment of sleep-related disorders such as Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA).There are three types of sleep apnea, namely obstructive (OSA), central (CSA), and a mixture of the two called mixed sleep apnea. Risk factors for OSA result in overweight, allergies, a small airway, and enlarged tonsils. Sleep doctor also treats other sleep-related disorders, namely insomnia, Restless legs syndrome, Periodic leg movement disorder, Narcolepsy, Circadian rhythm disorder, and a few more.  How to become a Sleep Doctor?
How to become a Sleep Doctor?
> - Spinal Cord Injury Specialist
 Spinal Cord Injury Specialist. Spinal cord Injury (SCI) specialists are rehabilitation medical doctors who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of people with spinal cord injuries. A spinal cord injury causes either temporary or permanent changes to its functions (loss of muscle function, sensation loss, pressure sores, infections, or breathing problems).In most cases, spinal cord damage directly results from physical trauma, including car accidents, gunshot wounds, falls, or sports-related injuries. First Become a Neurosurgeon? Then Certification for SCiM-SCIS?
Spinal Cord Injury Specialist. Spinal cord Injury (SCI) specialists are rehabilitation medical doctors who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of people with spinal cord injuries. A spinal cord injury causes either temporary or permanent changes to its functions (loss of muscle function, sensation loss, pressure sores, infections, or breathing problems).In most cases, spinal cord damage directly results from physical trauma, including car accidents, gunshot wounds, falls, or sports-related injuries. First Become a Neurosurgeon? Then Certification for SCiM-SCIS?
> - Sports Medicine Specialist
 Sports Medicine Specialist. Sports medicine specialists are trained medical doctors in the treatment of people who have injuries to their bones, muscles, joints, tendons, or ligaments that result from physical activity (such as Sports).The injuries include cartilage tears, ligament ruptures of the knee, and shoulder, knee, or wrist problems.
Sports Medicine Specialist. Sports medicine specialists are trained medical doctors in the treatment of people who have injuries to their bones, muscles, joints, tendons, or ligaments that result from physical activity (such as Sports).The injuries include cartilage tears, ligament ruptures of the knee, and shoulder, knee, or wrist problems.  How to become a Sports Medicine Physician?
How to become a Sports Medicine Physician?
> - Surgeon
 Surgeon. A surgeon is a physician trained in performing operations that involve treating injuries, removing infected body parts, and reconstructing missing or damaged tissues or organs.
Surgeon. A surgeon is a physician trained in performing operations that involve treating injuries, removing infected body parts, and reconstructing missing or damaged tissues or organs.
How to Become a Surgeon?
Medical doctors who treat and specialize in the surgery of colon/rectum are called colon and rectal surgeons.
How to Become Colo/Rectal Surgeons?
> - Thoracic Surgeon
 Thoracic Surgeon. Thoracic Surgeon is specialized in chest, heart, and lung surgeries. Thoracic surgeons may further specialize in one area, such as heart or lung surgery, or in a sub-specialty of that area, such as coronary artery bypass surgery. The thoracic surgeries include open-heart surgery, off-pump bypass surgery, robot-assisted heart surgery, Pediatric cardiovascular surgery (i.e., children’s heart surgery), lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS), and more. How to become a Thoracic Surgeon?
Thoracic Surgeon. Thoracic Surgeon is specialized in chest, heart, and lung surgeries. Thoracic surgeons may further specialize in one area, such as heart or lung surgery, or in a sub-specialty of that area, such as coronary artery bypass surgery. The thoracic surgeries include open-heart surgery, off-pump bypass surgery, robot-assisted heart surgery, Pediatric cardiovascular surgery (i.e., children’s heart surgery), lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS), and more. How to become a Thoracic Surgeon?
> - Urologist
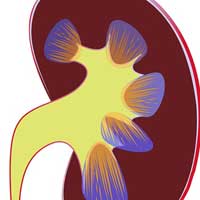 Urologist. Urologists specialize in diagnosing and treating disorders affecting the male and female urinary tract. In addition to that, urologists are also knowledgeable in treating patients with prostate cancer and other diseases that affect sexual health and fertility.
Urologist. Urologists specialize in diagnosing and treating disorders affecting the male and female urinary tract. In addition to that, urologists are also knowledgeable in treating patients with prostate cancer and other diseases that affect sexual health and fertility.
How to become a Urologist?
> - Vascular Surgeon
 Vascular Surgeon. Vascular surgeons are medical physicians who specialize in the diagnosis, medical management, and surgical treatment of diseases with the blood vessels (vascular diseases).The scope of vascular surgery encapsulates surgery of veins (for May-Thurner syndrome and varicose veins), the aorta, carotid arteries, and lower extremities, including the iliac, femoral, and tibial arteries. In some parts of the world, vascular surgery also includes dialysis access surgery and transplant surgery. How to become a Vascular Surgeon?
Vascular Surgeon. Vascular surgeons are medical physicians who specialize in the diagnosis, medical management, and surgical treatment of diseases with the blood vessels (vascular diseases).The scope of vascular surgery encapsulates surgery of veins (for May-Thurner syndrome and varicose veins), the aorta, carotid arteries, and lower extremities, including the iliac, femoral, and tibial arteries. In some parts of the world, vascular surgery also includes dialysis access surgery and transplant surgery. How to become a Vascular Surgeon?
> - Veterinarian
 Veterinarian While all other doctors are responsible for treating humans, veterinarians are responsible for treating sick animals. Veterinary Doctors are included here because they are Doctors! A veterinary doctor (usually called a vet) practices veterinary medicine by treating illnesses, ailments, and injuries in animals (pets and cattle). Vets provide the diagnosis and treatment in the forms of prescribing medicines or performing surgeries and aftercare. Vets rely on the clinical symptoms of their diagnosis as animals cannot speak.
Veterinarian While all other doctors are responsible for treating humans, veterinarians are responsible for treating sick animals. Veterinary Doctors are included here because they are Doctors! A veterinary doctor (usually called a vet) practices veterinary medicine by treating illnesses, ailments, and injuries in animals (pets and cattle). Vets provide the diagnosis and treatment in the forms of prescribing medicines or performing surgeries and aftercare. Vets rely on the clinical symptoms of their diagnosis as animals cannot speak.
This Doctor List is up to date as of 11/01/2024
